High-speed CAN vs. Diagnostic CAN
For vehicle CAN input, the VBOX Video HD2 requires a connection to the high-speed CAN bus of a vehicle.
You can configure VBOX Video HD2 to record both diagnostic CAN and high-speed CAN. The two types of CAN signals do not work the same way and will be configured and recorded as completely separate inputs.
The Diagnostic CAN is available on the OBD connector via a diagnostic tool. The high-speed CAN bus can sometimes be accessed at the OBD connector, but this is not the case for all vehicles and it is becoming less common in modern models due to gateways installed by manufacturers.

If you want to log diagnostic CAN, you will need to use the OBD Solutions OBDLink Module (RLACS228).
High-speed CAN
With high-speed CAN, also commonly known as CAN 2.0, CAN devices (e.g. ECUs) constantly broadcast their data onto the CAN network, and any other device on the network can read the data in real time.
When you connect the VBOX Video HD2 to the vehicle CAN bus via the unterminated CAN interface cable (RLCAB015L), the unit will act as another CAN device on the network listening for data. Alternate connectors, such as the clip-on CAN bus interface (RLACS182), read the CAN data inductively, without adding any extra load to the vehicle's CAN bus. With either of these connection methods, the VBOX Video HD2 can record high-speed CAN data from the vehicle bus.
By loading a CAN database file, or selecting one of the models from our Vehicle CAN Database, you can configure the VBOX Video HD2 to log selected channels from the vehicle CAN bus at a higher resolution than what you get with diagnostic CAN. You can find further information about how to configure the CAN inputs via the VBOX Video HD2 Setup software here.
| Note: If a particular model is not currently found in our Vehicle CAN Database, you can request further additions by selecting the Send a CAN request option here. |
Diagnostic CAN
Diagnostic CAN, also commonly referred to as OBDII or PIDs, is based on a system of “request” and “reply”. The OBDLink module sends a request for the data of a particular channel to the vehicle and then awaits a response. The vehicle will send the current value of the requested channel back to the module if it is able. Once the response is received, the next request can be sent by the module.
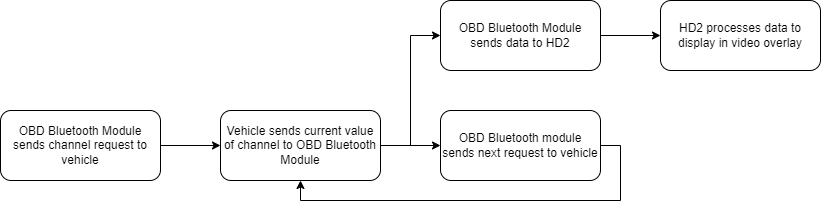
Because diagnostic CAN wasn’t designed for speed or performance, you can end up with slower or low-resolution data. The more channels you select, the more requests the module sends and the lower the resolution of the data will be, particularly when you compare this to high-speed CAN data.
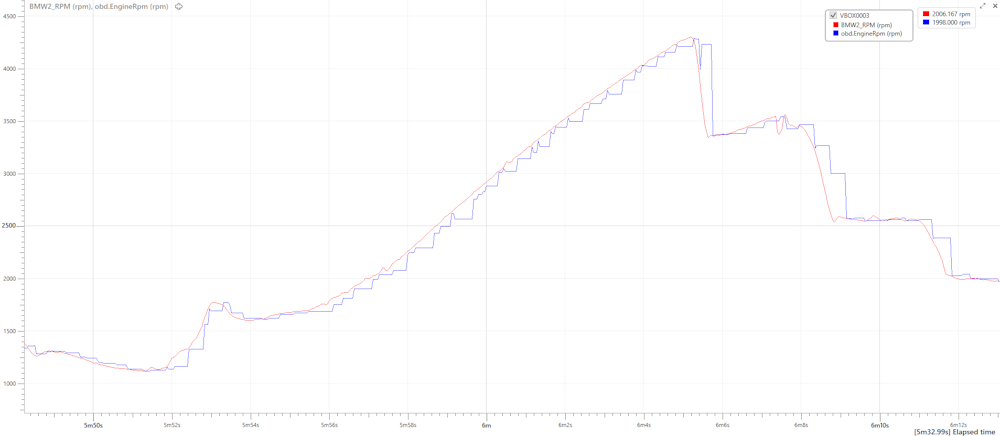
This graph shows the Engine RPM channel, where OBD data is blue and the high-speed CAN data is red. You can see that the OBD data has a slower update rate and lower resolution when all OBD channels have been selected in the HD2 configuration.
When you configure the OBD input channels in the VBOX Video HD2 Setup software, you can set the priority for each selected message. This priority affects how often that channel is requested. For example, a priority of 1 is requested 64 times more frequently than a priority of 7. Fast-changing variables, such as engine RPM, should have a high priority, while slow-changing variables, such as fuel level, should have a low priority.
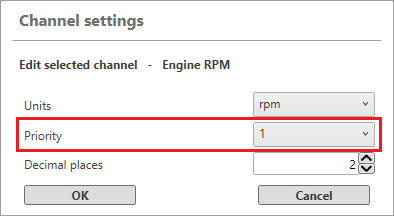
While adjusting the priority can help optimise the resolution of diagnostic CAN, the actual update frequency depends on the vehicle and the number of selected channels. You can find additional information about how to configure the VBOX Video HD2 OBD channels here.
| Note: Not all OBD channels may be supported by your vehicle. The OBDLink module is only able to detect signals that are present on the bus, which is dictated by the vehicle manufacturer. |
